IPsec VPN: Understanding IKE Phase 1 Main Mode
Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) is a framework that helps to protect the IP traffic on network layer over the untrusted network (Internet)
IiWhy IPsec?
Because the IP protocol itself doesn't have any security features at all. It protects the IP traffic by introducing confidentiality, integrity, authentication & anti-replay features
Why consider IPSec as a framework?
IPsec is a complete suite of protocols with predefined rules to protect IP traffic over the internet. It offers a variety of protocols which includes :
IPsec Protocols:
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
Authentication Header (AH)
ESP + AH
Encryption Algorithms:
Data Encryption Standard (DES)
Triple DES (3DES)
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
Authentication / Hashing algorithms:
Message Digest version 5 (MD5)
Secure Hashing Algorithm (SHA)
Hash-based message authentication code (HMAC)
Diffie Hellman Groups:
DH Group 1 (DH1)
DH Group 2 (DH2)
DH Group 5 (DH5)
DH Group 14 (DH14)
DH Group 15 (DH15), etc.
NOTE: Higher group no. = strength of the key used in the key exchange process
What does the whole process of IPsec VPN negotiation consists of?
| INITIATION | Creation of the tunnels is triggered either because of the identification of traffic through the configured policy or routing (GRE over IPSec/ DMVPN with IPSec) |
| IKE Phase 1 | ISAKMP tunnel |
| IKE Phase 2 | IPSec tunnel |
| Data transmission | user data is protected as per the negotiated security associations (SAs) and is sent via IKE phase 2 tunnels |
| Termination | The IPSec tunnel will be terminated when there is no user data to protect or the tunnel is explicitly terminated. |
NOTE: In VPN, logical connection = tunnel.
What is IKE?
Internet Key Exchange (IKE) is the protocol used to establish an IPSec tunnel.
There are 2 versions of IKE:
IKEv1 (version 1)
IKEv2 (version 2)
In this article, we are going to focus on IKEv1 ISAKMP main mode.
IKE Phase 1 | ISAKMP tunnel
IKE (Internet Key Exchange) Phase 1 is the first stage of the IPSec VPN (Virtual Private Network) connection (tunnel), and its main purpose is to establish a secure tunnel that we can use for IKE Phase 2 tunnel.
used for secure management plane traffic transmission.
IKEv1 phase 1 tunnel can be established using 2 different modes:
| Mode | No. of messages | Description |
| Main Mode | 6 | - used when peer IP is static & provides identity protection |
| Aggressive Mode | 3 | - used when peer IP is dynamic & doesn't provide identity protection |
Let's discuss IKEv1 Main Mode.
MAIN MODE :
The IKE Phase 1 protocol has 3 main components:
1. Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP):
protocol framework describes the procedure & packet format
used for negotiating and defining SAs between peers
provides a framework for authentication, confidentiality, integrity, and key exchange
uses UDP port = 500 | 4500 (in case of NAT-T ) or TCP port = 10000 in case of IPsec over TCP
2. Diffie-Hellman (DH) key exchange algorithm:
- It is an asymmetric algorithm used to generate the symmetric key over the untrusted network on VPN peers.
3. Identification Payload:
- payload which contains the information by which the IPsec peers identify each other in main mode messages 5 & 6.
Breakdown of IKE Phase 1:
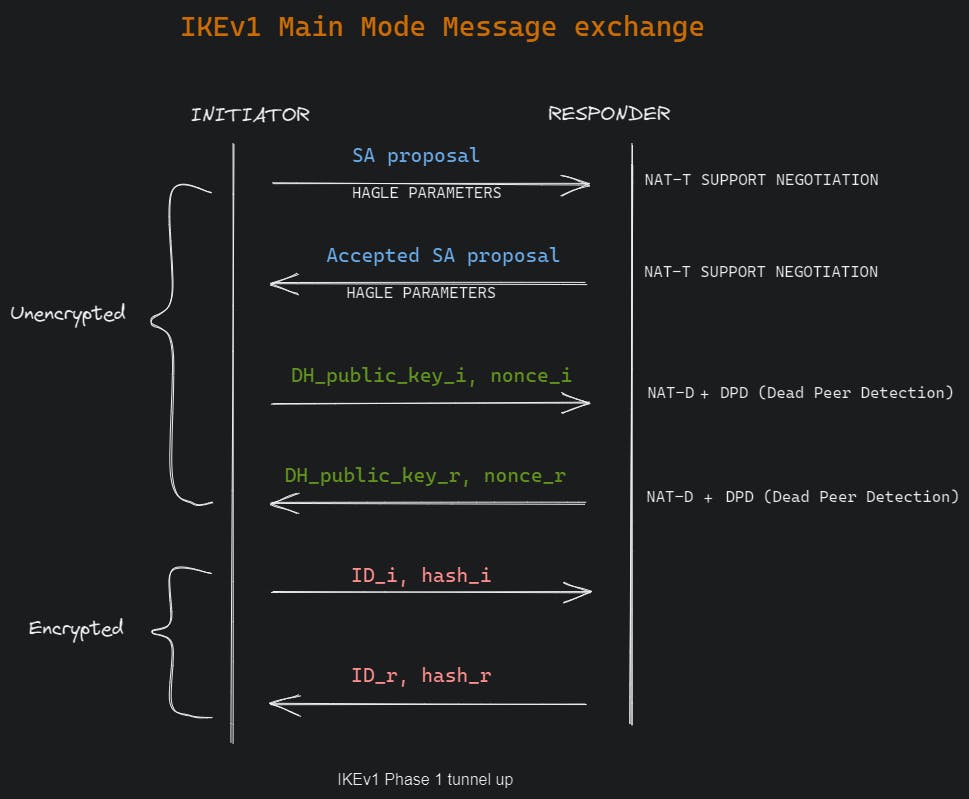
Negotiation | Main Mode Message 1 & 2:
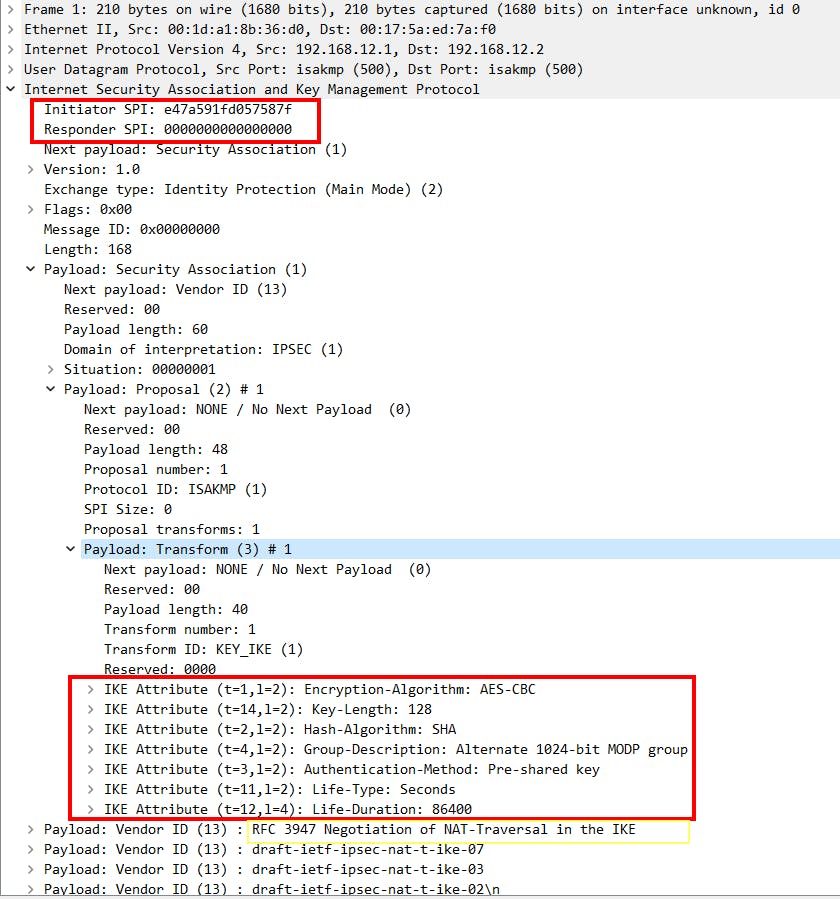
- IKE phase 1 negotiation is performed by sharing the security association (SA) parameters referred to as HAGLE which is an informal abbreviation for :
| SA name | Description |
| Hashing | MD5 / SHA |
| Authentication | pre-shared key/digital certificate |
| DH Group | Higher group number \= higher strength of the key = more secure |
| Lifetime | lifetime of IKE phase 1 tunnel; default value = 86400 sec (1 day) |
| Encryption | encryption algorithm: DES/3DES/AES |
NAT-T support negotiation happens in these messages:
Main mode message 1:
- Main mode message 2:
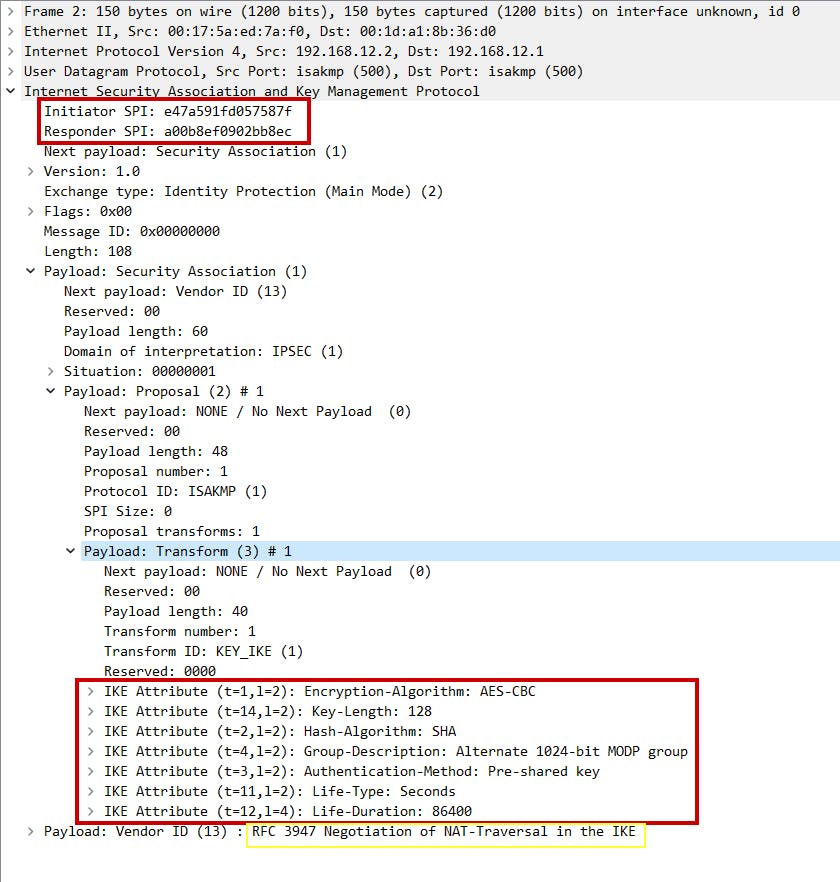
Point to remember: Lifetime is the only parameter that can be configured with different values on VPN peers and the lower lifetime value will be negotiated among them.
DH key exchange | Main Mode message 3 & 4:
peers will use the agreed DH group to perform key exchange and will have the shared key ultimately.
NAT-D (NAT detection) & DPD (Dead Peer Detection) are also performed in these messages.
Main mode message 3:
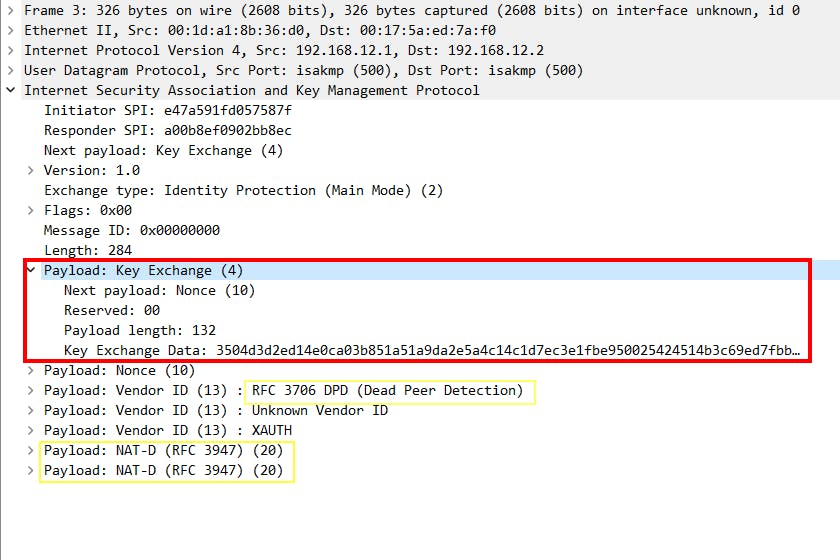
Main mode message 4:
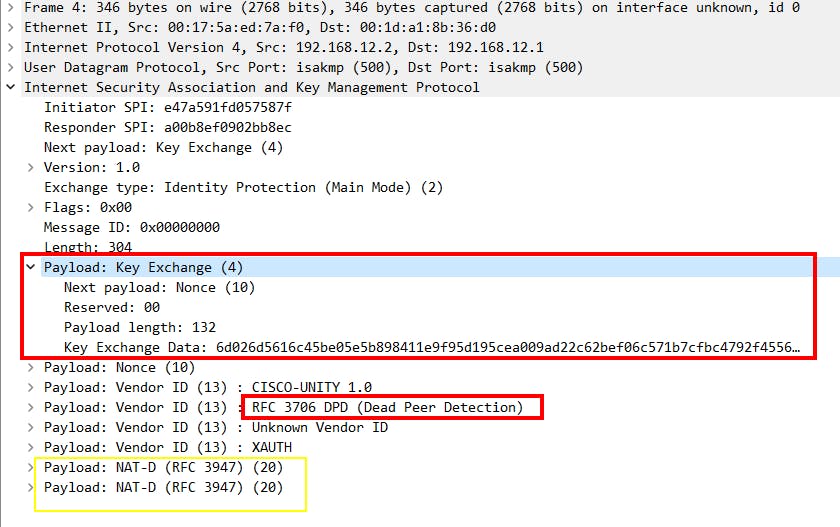
Authentication | Main Mode message 5 & 6:
pers will authenticate each other using the negotiated authentication method (in our case, it is a pre-shared key).
Main mode messages 5 & 6 are encrypted. So, you won't be able to see the content but you can refer to the packet flow diagram at the start of this section.
End result is IKE phase 1 tunnel/ ISAKMP tunnel is up and is bidirectional
Main mode message 5:
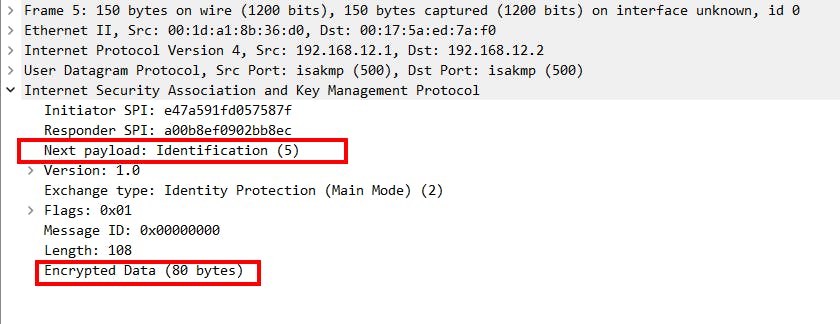
Main mode message 6:
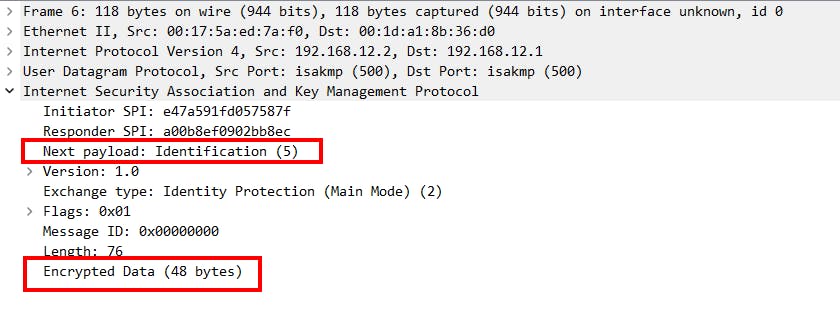
The above-specified steps can be performed using aggressive mode and require only 3 messages instead of 6 messages which will be covered in the next article.
REFERENCES:
